Human GM-CSF Immunoassay/SEKH-0057
- Price:Negotiable
Product Detail
BACKGROUND
Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF), also known as CSF-2, is a
pleiotrophic 30 kDa member of the Common beta Chain (βc) cytokine family that also includes IL-3 and IL-5. GM-CSF adopts an α-helical configuration with two intrachain disulfide bonds. It is secreted by a wide variety of activated immune, mesenchymal, and epithelial cell types and circulates as a variably glycosylated monomer. It is upregulated in multiple cell types during inflammation including encephalitogenic T cells, allergen exposed lung endothelial cells, and IgE activated mast cells. Mature human GM-CSF shares 54% and 63% amino acid sequence identity with mouse and rat GM-CSF, respectively.
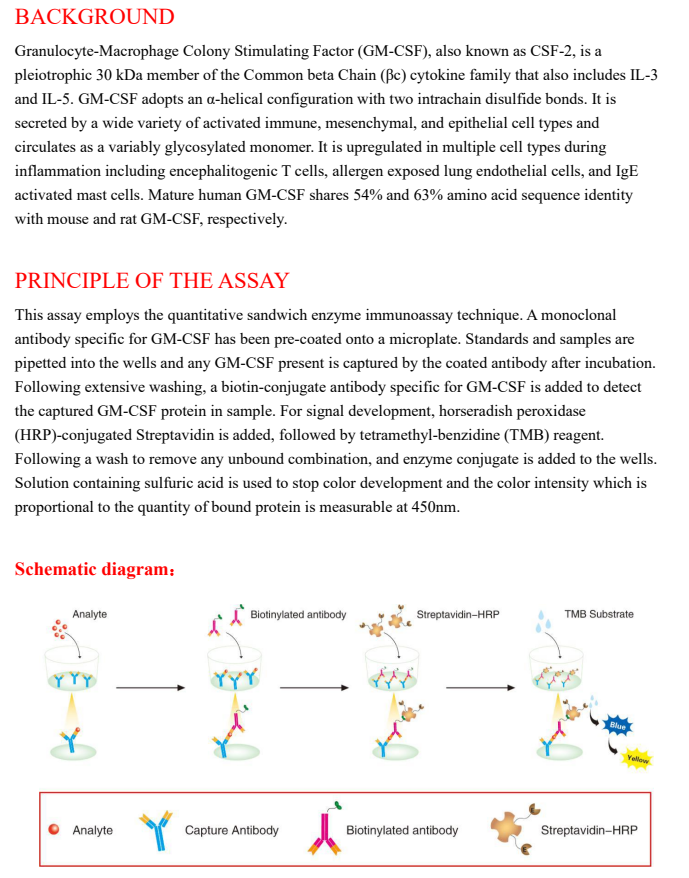
PRINCIPLE OF THE ASSAY
This assay employs the quantitative sandwich enzyme immunoassay technique. A monoclonal
antibody specific for GM-CSF has been pre-coated onto a microplate. Standards and samples are pipetted into the wells and any GM-CSF present is captured by the coated antibody after incubation. Following extensive washing, a biotin-conjugate antibody specific for GM-CSF is added to detect the captured GM-CSF protein in sample. For signal development, horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated Streptavidin is added, followed by tetramethyl-benzidine (TMB) reagent. Following a wash to remove any unbound combination, and enzyme conjugate is added to the wells. Solution containing sulfuric acid is used to stop color development and the color intensity which is proportional to the quantity of bound protein is measurable at 450nm.